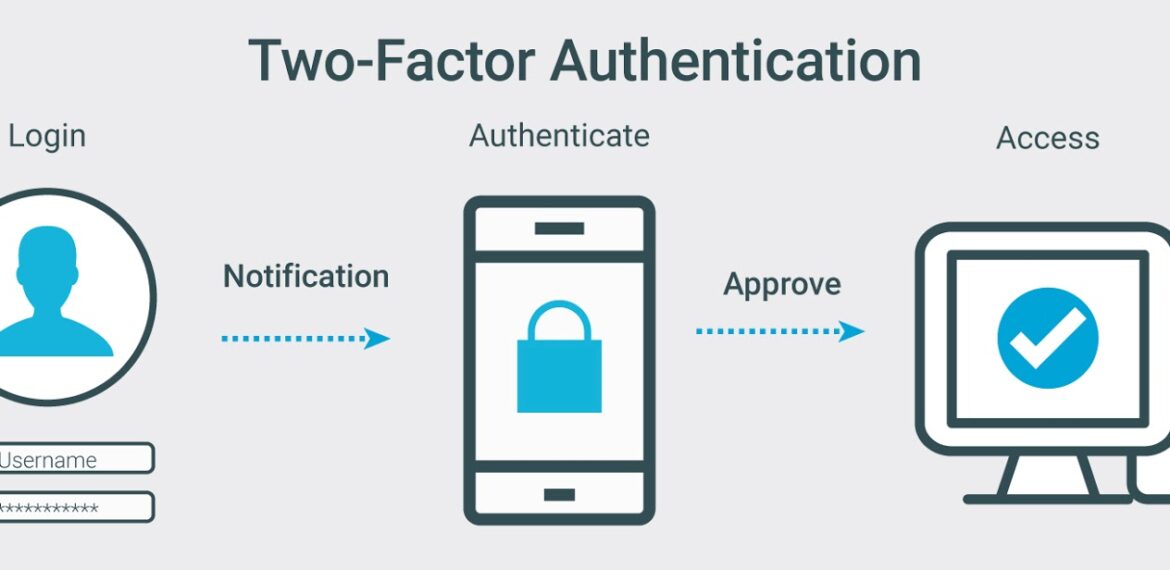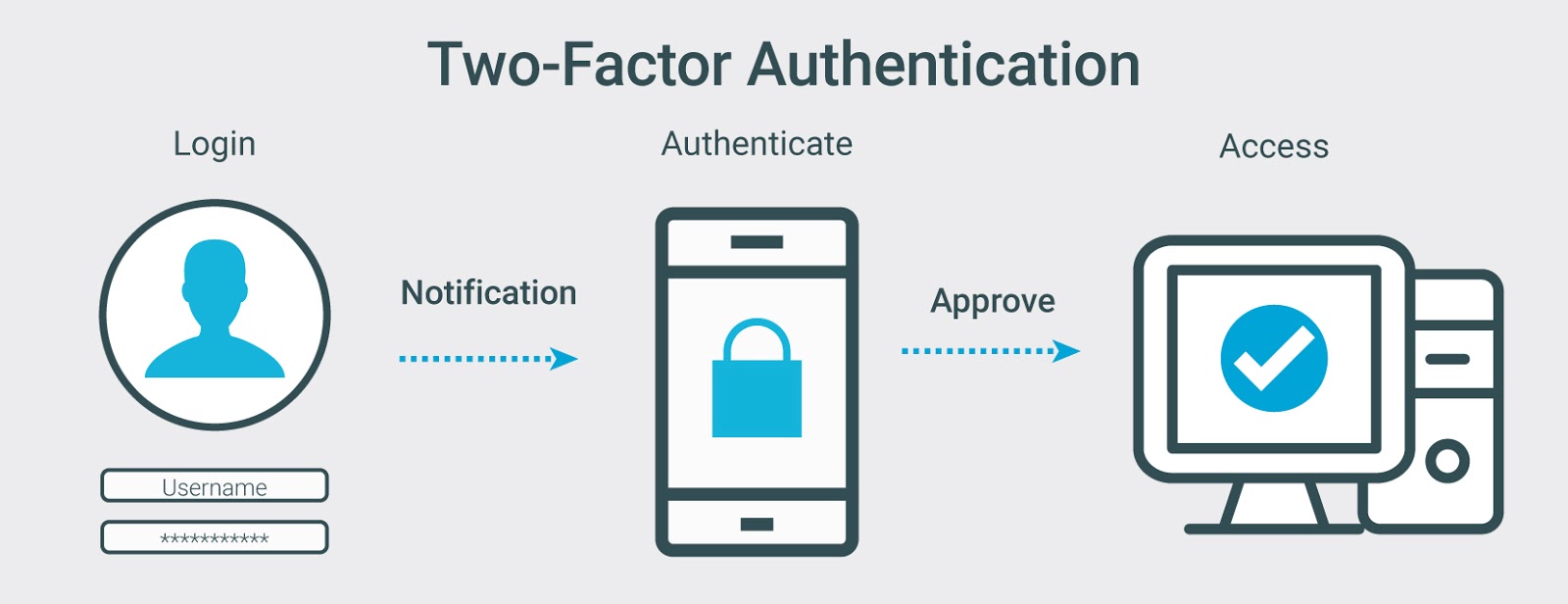
Two-factor authentication (2FA), once in a while referred to as two-step verification or dual-factor authentication, is a security method in which users provide two one-of-a-kind authentication factors to verify themselves. This procedure is done to better shield both the user’s credentials and the resources the person can access. Two-factor authentication offers a greater degree of security than authentication techniques that rely on single-factor authentication (SFA), in which the user provides only one element — typically, a password or passcode. Two-factor authentication strategies count on a person offering a password, as properly as a 2d factor, usually both a protection token or a biometric factor, such as a fingerprint or facial scan.
Two-factor authentication provides an extra layer of safety to the authentication procedure through making it harder for attackers to reap access to a person’s gadgets or online debts because understanding the victim’s password on my own is not adequate to pass the authentication check. Two-factor authentication has long been used to control get admission to to touchy systems and data, and on line service companies are increasingly the use of 2FA to shield their users’ credentials from being used through hackers who have stolen a password database or used phishing campaigns to attain user passwords.
What are authentication factors?
There are quite a few special approaches in which any individual can be authenticated the usage of extra than one authentication method. Currently, most authentication techniques rely on know-how factors, such as a typical password, while two-factor authentication techniques add either a possession component or an inherence factor.
Authentication factors, listed in approximate order of adoption for computing, include the following:
- A knowledge factor is something the user knows, such as a password, a PIN (personal identification number) or some other type of shared secret.
- A possession factor is something the person has, such as an ID card, a safety token, a cellphone, a mobile machine or a smartphone app, to approve authentication requests.
- An inherence factor, greater normally known as a biometric factor, is something inherent in the user’s bodily self. These may additionally be non-public attributes mapped from physical characteristics, such as fingerprints authenticated through a fingerprint reader. Other frequently used inherence elements consist of facial and voice recognition. They also include behavioral biometrics, such as keystroke dynamics, gait or speech patterns.
- A location factor, usually denoted by the location from which an authentication attempt is being made, can be implemented by restricting confirmation endeavors to explicit gadgets in a specific area or, all the more usually, by following the geographic wellspring of a verification endeavor dependent on the source Internet Protocol (IP) address or some other geolocation data, for example, Global Positioning System (GPS) information, gotten from the client’s cell phone or other gadget.
- A time factor restricts user authentication to a specific time window in which logging on is accepted and restricts get admission to to the machine backyard of that window.
It be referred to that the considerable majority of two-factor authentication strategies be counted on the first three authentication factors, though structures requiring higher protection may additionally use them to enforce multifactor authentication (MFA), which can count number on two or extra impartial credentials for greater secure authentication.
Sample Authenticator App: Google Authenticator